With a Keenetic router, it's possible to remotely turn on home network computers via the web GUI or a mobile app by exploiting the Wake-on-LAN (WOL) technology.
Wake-on-LAN is a special option of the PC's boot firmware — BIOS or, on modern systems, UEFI, that allows you to power on the computer by sending a special signal (a so-called 'magic' packet) to that computer over the local network. A practical use case might be, for example, when you are in the office, you can remotely turn on your home PC. The computer must be in sleep mode, and it must have Wake-on-LAN enabled beforehand.
In some Wi-Fi devices (wireless adapter, smart TV) this technology is called WoWLAN (Wake on Wireless LAN).
To 'wake up' your computer, you need to log in to the Keenetic device web interface or open the Keenetic mobile app, select the PC in a list of home network devices and click the 'Wake on LAN' button.
Importante
To boot up from a Wake-on-LAN signal, the motherboard and the network adapter of a PC must be compatible with this feature. Modern motherboards might be pre-configured to support this function on an onboard NIC. For information on configuring the BIOS/UEFI settings and enabling the Wake-on-LAN ability, please refer to your motherboard's user manual. The BIOS, operating system, and network interface card settings are for advanced computer users only. Our technical support is only available to help you set up your Keenetic router. Please get in touch with the respective manufacturer's support service for BIOS, operating system, and network adapter settings.
The Wake-on-LAN feature is not available in repeaters that are connected to another manufacturer's master router! Wake-on-LAN works on Keenetic in the main ‘Router’ mode or as part of a Mesh Wi-Fi system when a Keenetic main router is present.
Here is an example of how the Wake-on-LAN function can be launched using the Keenetic router.
Access your computer's BIOS or UEFI setup interface. It is usually achieved by pressing the
F2orDelkey on a keyboard during the PC boot process before the operating system starts to load. Enable WOL-related BIOS settings. Refer to your motherboard user's manual for this. Common names for WOL settings are: 'Power On By Onboard LAN', 'Remote Wake Up', 'Wake On LAN', etc. Pay attention to the BIOS using the 'S1 State' power saving mode, not 'S3 State'. 'S3 State' is a more energy-efficient mode, and in most cases, it turns off the power of the network card, which means that it will not be able to receive a magic packet. If the motherboard supports ErP standard, it also should remain disabled for the same reason as S3 sleepIn your computer's operating system, you need to configure the network adapter. Open the Windows settings. Go to the Network and Internet menu, and on the Status tab in the Network Settings Changes section, click Change Adapter Settings. In the Network Connections window that appears, right-click the Ethernet Connection icon and then click Properties. Click the 'Configure...' button in the network adapter properties window.
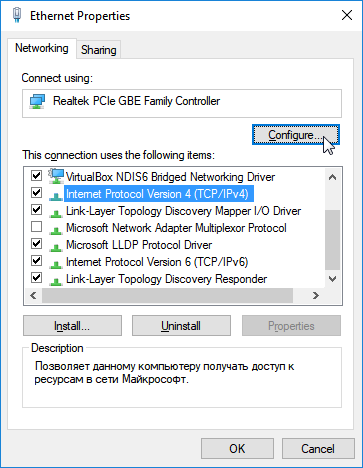
Go to the 'Advanced' tab.
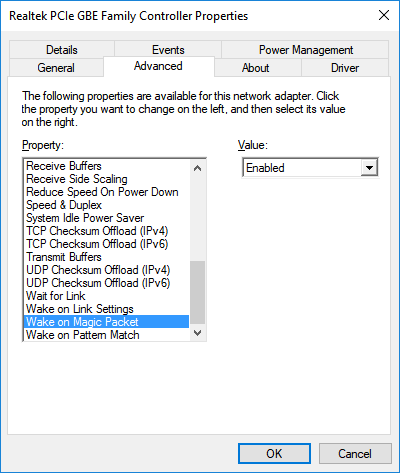
Unless the instruction on enabling the WOL capability from the NIC driver manufacturer states otherwise, we recommend turning on all the WOL-related settings. Set everything similar to: Wake on Magic Packet; Wake on pattern match; Wake From Shutdown; Wake-Up; Resume on LAN; Shutdown Wake-On-Lan (WOL);
Enabled.Please note we're citing mostly frequent names of these parameters, while the network adapter driver manufacturer might use different naming.
Next, go to the 'Power Management' tab and enable the options to allow the computer to wake from sleep (standby) mode — 'Allow this device to wake the computer' and 'Only allow a magic packet to wake the computer'.
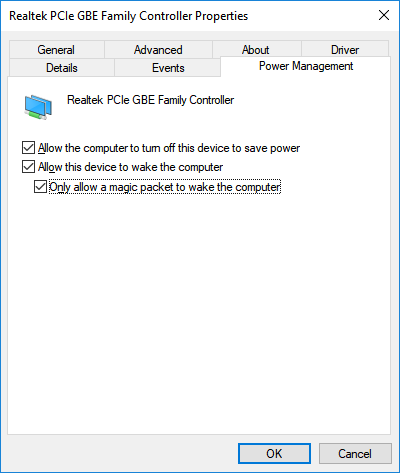
Then shut down the computer by putting it into sleep mode.
To ensure that the BIOS and network adapter are configured correctly, connect to the Keenetic web interface from another device (such as the Internet or another home network computer). The Dashboard's Network Ports information panel should show the active connection of a PC in sleep mode. Typically, such a connection is in 'FDX 10 M' operating mode (full-duplex,
10 Mbps). In our case, the PC in sleep mode is connected toport 2.
Also pay attention to the Ethernet port on the network adapter. There are usually one or two information LEDs next to it, indicating the connection and data transfer. When the PC is switched off, the LED usually blinks, i.e. the network adapter is powered on and ready to receive the magic package.

This completes the computer setup.
Now, open the router's web interface. To connect from the Internet, use the KeenDNS service, which allows you to get a permanent and easy to remember Internet address for Keenetic. With the help of the KeenDNS service, you can connect remotely to the web interface of your Keenetic router even if you use a private IP address to access the Internet. You can also use a secure VPN connection for a remote connection to the router.
Importante
The option to '
wake up' the computer only works under an administrator user account (i.e. when read-only access to the router settings is not used).Go to the 'Client lists' page. You can wake your computer up, be it a registered or unregistered home network device. Click on the entry of the desired device and then click on the 'Wake on LAN' button.

After a
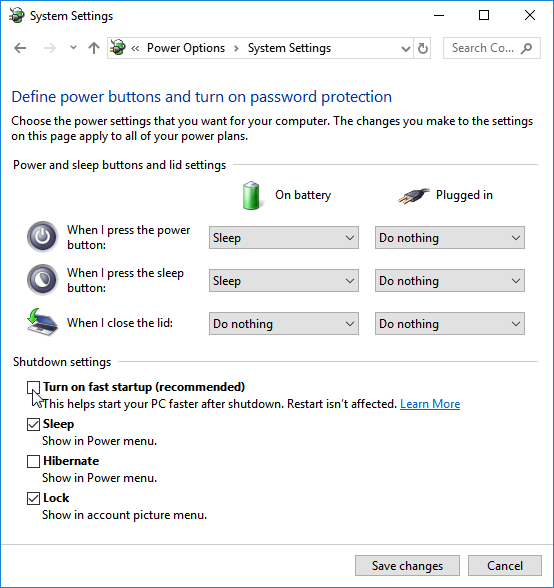
few minutes, check if the computer has powered on. When the PC is switched on, it should appear in the web interface in the 'Client lists' with the 'Online' status.If your computer does not turn on, try disabling the 'fast startup' feature in Windows. Go to Windows Settings in the System menu, move to Power & sleep section and click Additional power settings. Then, in the Power Options window that opens, go to 'Choose what the power buttons do' and in the 'Define power buttons and turn on password protection' window, click 'Change settings that are currently unavailable'. Then, in the 'Shutdown settings' section, disable the 'Turn on fast startup' option and click 'Save changes'.
You can wake up your computer not only from the Keenetic web interface. You can use our Keenetic mobile app for it too. You can find information and instructions on using the Keenetic app on our website under 'Keenetic App'.
In the 'My network' section, click on the device you want to '
wake up'. In our example, it is a laptop, which is connected to the router via Ethernet cable and is in the Offline status.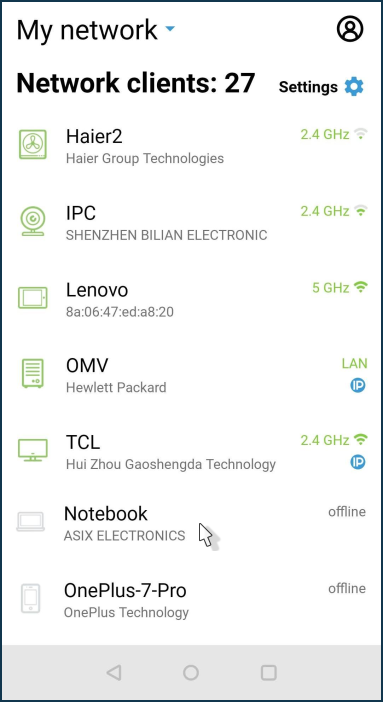
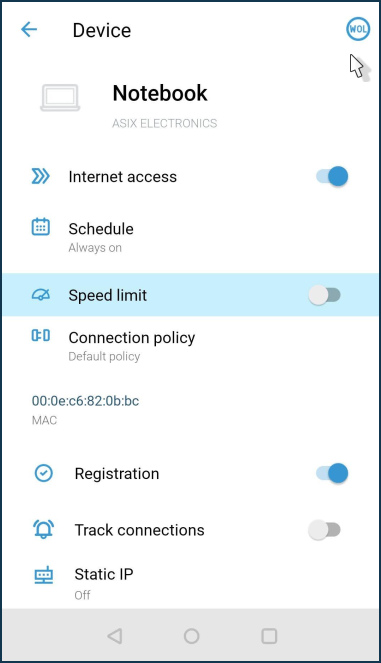
In the upper right corner of the screen, click the 'WOL' icon.
A special WOL packet will be sent to the device.
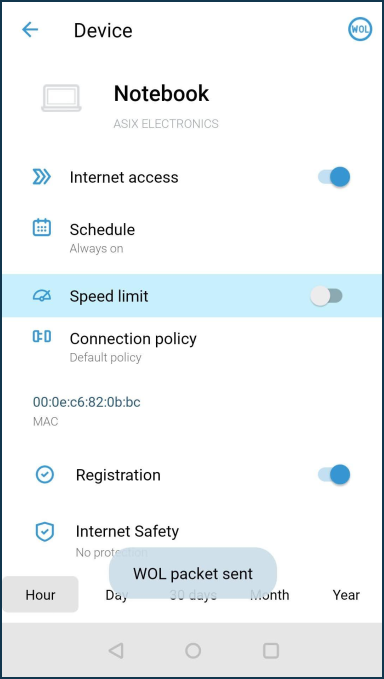
More information can be found in the instructions 'Waking up a computer with WOL from the Keenetic app'.
If the settings on the PC have been made correctly, the device will come out of hibernation mode and turn on. After a while, the computer will appear in the 'My network' section as Online.
If the above settings and recommendations do not work, please check the router's system log. Go to the Diagnostics page, in the System Log section, click Show log. You should be able to find the entry similar to the following:

The record indicates that the Keenetic has sent a special '
magic' wake-up packet to the device with the specified host MAC address.If you can see the message above, it is recommended to check all the Wake-on-LAN settings on your computer again. To set up your BIOS, operating system and network adapter, please contact the support service of the respective manufacturer.
Nota
The option of using Wake-on-LAN discussed in this article is secure because there is no need to open additional ports on the WAN side of the router's firewall. When using some Internet services that can send 'magic' packets to turn on computers, it is required to open the UDP/9 port on the router, proving a security breach.
Please note, if you use Giant (KN-2610), Titan (KN-1810) or Hero (KN-1010/1011) as a repeater, do not connect the patchcord from the main router to the repeater to the combined RJ-45/SFP WAN-port ‘0’, as in this case WoL will not work for network devices connected to this repeater. For correct WoL operation, connect the patch cord from the main router to any free network port 1 - 4, which is intended for connection of home devices.