Accessing the USB modem's Web UI via the KeenDNS service
Remote access to the USB modem web interface
If you use a 4G/3G modem to access the Internet and it is connected directly to your Keenetic router's USB port, you can set up remote access to the USB modem web interface (CdcEthernet) by a domain name via the KeenDNS service.
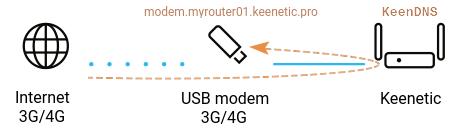
When using a private IP address on the router's external WAN port to access the Internet, you can set up access to the Keenetic web interface with the KeenDNS domain name service (via 'Cloud access'). In addition to accessing the Keenetic router's web interface, you can also set up remote access to some web applications on your home network (using 4th-level domain names).
From KeeneticOS 3.7 onwards, this can be done via the router's web interface. Add an access rule in the 'Access to web applications running on your network' section on the 'Domain name' page.
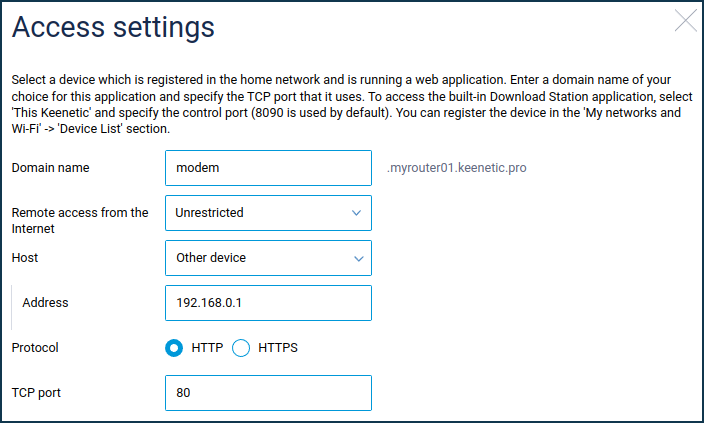
Give a suitable domain name, select the device registered in your home network on which the web application is running (or type in its IP address), select HTTP/HTTPS access protocol and specify the TCP port number that the web application uses. You can register devices in the Client lists section.
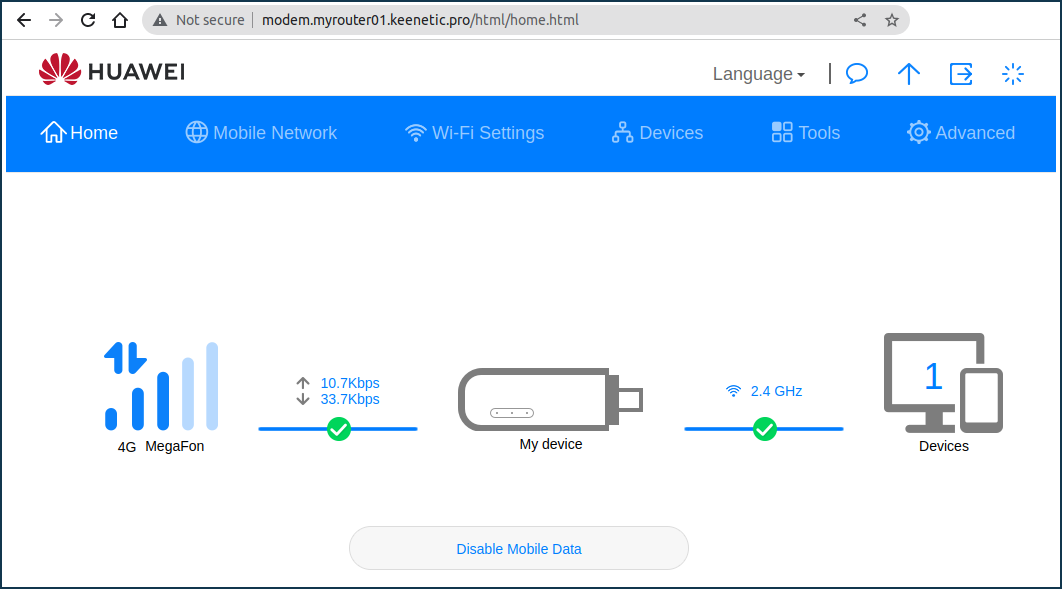
Then use a web browser to check if the USB modem web interface is accessible from the Internet. In our example, the modem is available at modem.myrouter01.keenetic.pro, where myrouter01 is your KeenDNS name.
Importante
The setting of access to the USB modem web interface via KeenDNS service in 'Cloud access' mode depends directly on the USB modem web interface implementation. On some USB modems, access to the web interface may be available only in the 'Direct access' mode.
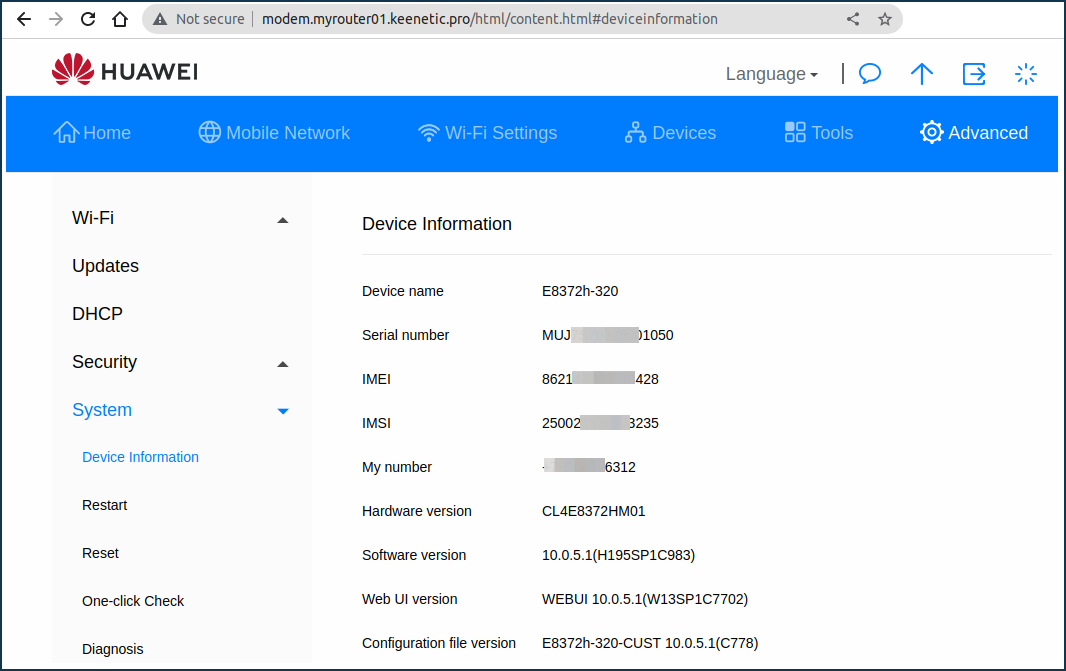
In our example, we have checked access to the Huawei E8372 modem:
Suggerimento
Usually, USB modems have an unsecured web interface, which can be accessed without login and password. It is not safe to leave remote access to such devices open. In KeeneticOS, it is possible to enable forced authentication when accessing such devices remotely using Keenetic.
When setting up access, select 'Password protected' in the 'Remote access from the Internet' field and then choose an account from the 'Users' section that appears.
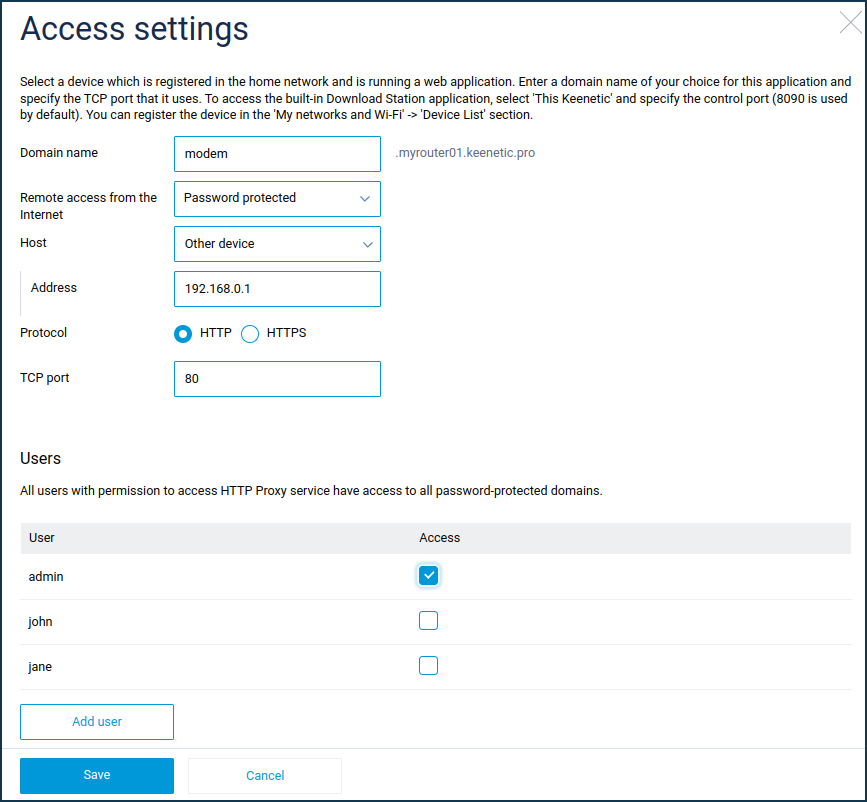
Now when you open modem.myrouter01.keenetic.pro in your web browser, you will see a login window asking you to enter your username and password. Only after you enter 'admin' and the appropriate password, Keenetic will redirect your request to the web interface of the device.
For more information, see the article Password protected remote access to a device with open Web UI via KeenDNS.
For Keenetic routers with KeeneticOS version 3.6 and lower, this configuration can only be done via the router's command line interface (CLI).
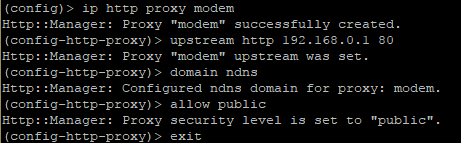
Let's look at an example. Execute the following commands:
ip http proxy modem upstream http 192.168.0.1 80 domain ndns allow public exit
where modem — the name for a 4th-level domain, 192.168.0.1 — USB modem IP address (this address may vary depending on the modem, e.g. Huawei modems often have 192.168.8.1), 80 — USB modem web interface port number.
To save the settings, run the command:
system configuration save
Nota
Due to hardware limitations, modem web interfaces may work differently. If remote access to a USB modem does not work for you, try using the command in the command line interface (CLI) of the router:
ip http proxy {name} preserve-host
Where {name} is the name for the KeenDNS 4th-level domain. This command has been added to KeeneticOS since version 2.13.
Suppose you use the address modem.myrouter01.keenetic.pro
Then the command would look like this:
ip http proxy modem preserve-host
Then check access and if it works, save the setting with the command:
system configuration save
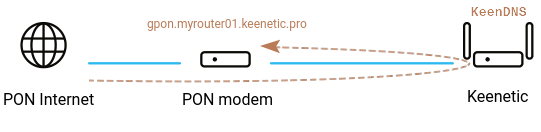
Remote access to GPON modem/router web interface
In the same way, you can set up remote access to the web interface of the GPON modem/router, which is used to connect to the Internet and behind which the Keenetic router is installed.
In the same way, you can set up remote access to the router's web interface. In the 'Network rules' menu on the 'Domain name' page, under 'Access to web applications running on your network', add an access rule.
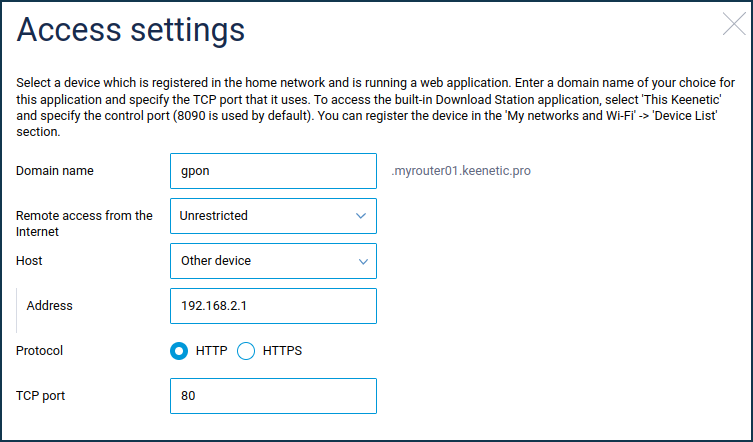
Choose a domain name, specify its IP address, and select the HTTP/HTTPS access protocol and the TCP port number that the web application uses.
Then use a web browser to check if the GPON modem/router web interface is accessible from the Internet. In our example, the web interface is available at gpon.myrouter01.keenetic.pro, where myrouter01 is your KeenDNS name.
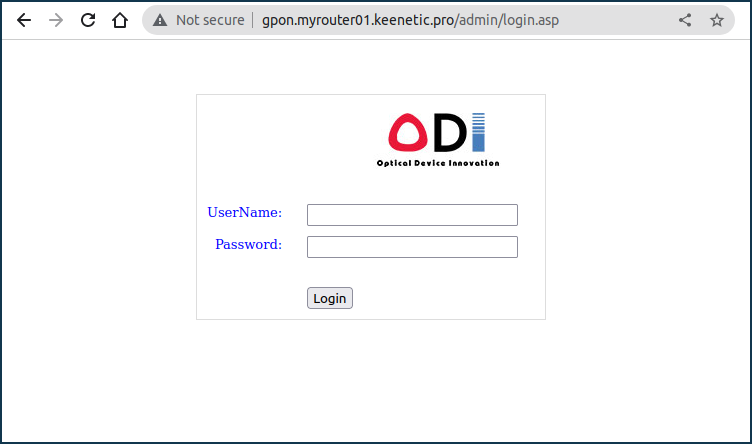
For Keenetic routers with KeeneticOS version 3.6 and earlier, such configuration is only possible via the router's command line interface (CLI).
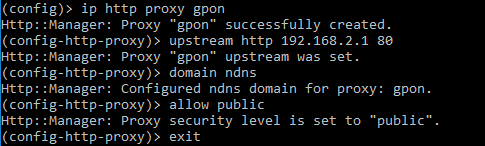
Let's look at an example. Execute the following commands:
ip http proxy gpon upstream http 192.168.2.1 80 domain ndns allow public exit
where gpon is the name for the 4th level domain, 192.168.2.1 is the IP address of the GPON modem, 80 is the GPON modem web interface port number.
To save the settings, run the command:
system configuration save