GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) is a technology for building broadband multi-service access networks over optical fibre. Currently, the number of subscribers connected to the Internet via GPON is actively growing (especially the growth of GPON networks is noticed in large cities).
In this article, we will look at examples of using a Keenetic router and optical GPON modem/router (also called ONT, Optical Network Terminal) together.
So, let's assume you already have a GPON modem/router installed in your flat and Internet access service connected, but you want to:
build your own home network, independent of the provider's router, and manage it yourself (create access lists, have your own DHCP server, set up the firewall, create a guest wireless Wi-Fi network, etc.);
to connect all home computers and other network devices (smartphone, tablet, TV) without cabling (or if possible, reduce the maximum length of cables);
expand the Wi-Fi coverage area and improve the signal quality (e.g. this can be relevant in remote rooms of the flat where the Wi-Fi signal is relatively weak, or when connecting a SMART TV over the wireless network, or when using the IP telephony service);
use the AdGuard DNS, CleanBrowsing, Cloudflare DNS, Neustar UltraDNS Public, OpenDNS and Quad9 Internet filter for home network users to ensure secure access to Internet resources;
increase the security of your home network; when you are connected to the Internet through your own router, no unauthorised person can access your home network;
use USB applications available for Keenetic routers:
USB storage networking (file server),
WebDAV server,
(S)FTP server,
VPN server,
DLNA server,
BitTorrent Transmission client,
network printing on a compatible USB printer.
All these tasks are possible if you have a Keenetic router.
Let's see a practical example of how to connect a Keenetic router to a GPON ONT. Assume that GPON ONT works as a router (it has NAT network address translation and a DHCP server for automatic IP address distribution from the 192.168.x.x subnet).
Two connection methods are possible:
via Ethernet cable (in this case, you will need to run a cable from the Keenetic router to the GPON ONT);
Via Wi-Fi (without an Ethernet cable).
Connection via Ethernet cable
Advantages: Reliable and fast connection.
Disadvantages: routing the Ethernet cable through the flat.
Option 1
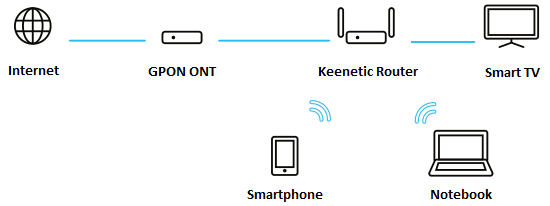
In this connection option, your Keenetic device will work as a regular router (NAT, DHCP server enabled) with a wireless Wi-Fi access point.
By default, Keenetic has the IP address 192.168.1.1, and in order for the device not to conflict with the GPON modem (assuming that it also distributes IP addresses from the 192.168.x.x subnet), you need to change the IP address of your Keenetic. To do this, connect to its web interface, go to the 'Home segment' page and in the 'IP settings' section, in the 'IP address' field, enter a private IP address other than 192.168.x.x (for example, set IP address 10.10.10.1) and click the 'Save' button.
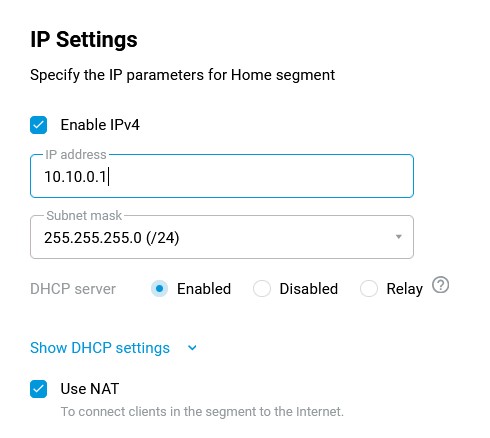
After changing the IP address of the network adapter, you will lose access to the web interface. To regain access, you will need to update the IP address of the network adapter (normally, it is sufficient to disconnect the Ethernet cable from the network adapter for a minute to re-acquire the IP address). Make sure that the IP address on your network adapter has now been assigned from the subnet 10.10.10.x and that the web interface of the Keenetic router is now accessible via the IP address 10.10.10.1.
Now you need to connect your Keenetic to the GPON modem with an Ethernet cable. Connect one end of the cable to Keenetic's WAN port (port 0; blue connector) and the other end to a free Ethernet port of the GPON modem.
Under default settings, the Keenetic router will automatically get an IP address from the GPON modem. You can verify that the IP address has been obtained on the 'System dashboard' page.
If the IP address has not been obtained, go to the 'Internet' -> 'Ethernet' page and make sure the 'IPv4 configuration' under 'IP and DNS settings' is set to 'Automatic (DHCP)'.
Next, configure the Wi-Fi access point for wireless clients to access the Keenetic router. For basic Wi-Fi access point settings, see the articles '2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network' and '5 GHz Wi-Fi network'.
With this connection option, you will create your own home network (10.10.10.x) independent from the GPON modem so you can manage it yourself (create access lists, have your own DHCP server, set up the firewall, create a guest Wi-Fi network, etc.). You will also be able to improve the quality (level) of the signal in the remote rooms of the flat, where the Wi-Fi signal is weak. You will be able to use AdGuard DNS, CleanBrowsing, Cloudflare DNS, Neustar UltraDNS Public, OpenDNS and Quad9 Internet filters for home network users to ensure secure access to Internet resources.
Option 2
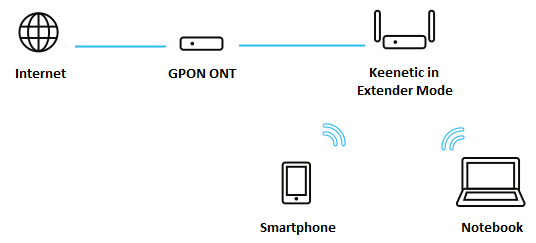
Consider a scenario where the Keenetic router is connected to the GPON modem using an Ethernet cable. One end of the Ethernet cable must be connected to the Ethernet port on the GPON modem, and the other end to any free port on the router. Keenetic will need to be set up in the optional 'Extender Mode'. In this mode, the Keenetic will be a simple 5-port Ethernet switch with a wireless Wi-Fi access point, with NAT and DHCP server disabled. You can also disable the Wi-Fi hotspot if required.
Computers and network devices connected to the Keenetic device via Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi will receive IP addresses from the GPON modem, i.e. all devices in your home network will be on the same subnet.
DHCP server must be enabled on the GPON modem for the router to work properly in Extender Mode.
Once Extender Mode is enabled, the router's web interface will not be available at its previous address (192.168.1.1 or my.keenetic.net). It will be accessible via the new IP address given by the GPON modem. This IP address can be viewed in the GPON modem web configurator (or by using an application to scan and identify LAN-connected devices).
On Keenetic in Extender Mode, you can use USB applications available for Router Mode (USB drive networking, DLNA, BitTorrent Transmission client, network printing on a compatible USB printer).
Connecting via Wi-Fi wireless network
Advantages: No need to run an Ethernet cable.
Disadvantages: Reduced real connection speed due to the nature of Wi-Fi technology.
Option 1
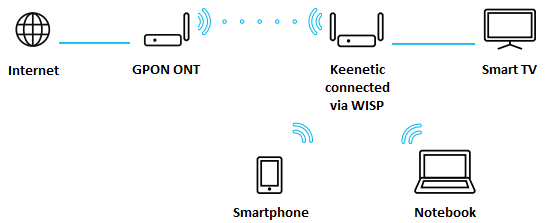
With this option, Keenetic will be running its WISP (Wireless ISP) connection. With this connection, Keenetic will work as a regular router (NAT, DHCP server enabled) with a wireless Wi-Fi access point and will use Wi-Fi client mode to connect to the GPON ONT's wireless network.
By default, Keenetic has the IP address 192.168.1.1, and in order for the device not to conflict with the GPON modem (assuming that it also distributes IP addresses from the 192.168.x.x subnet), you need to change the IP address of your Keenetic. To do this, connect to its web interface, go to the 'Home segment' page and in the 'IP settings' section, in the 'IP address' field, enter a private IP address other than 192.168.x.x (for example, set IP address 10.10.10.1) and click the 'Save' button.

After changing the IP address of the network adapter, you will lose access to the web interface. To regain access, you will need to update the IP address of the network adapter (normally, it is sufficient to disconnect the Ethernet cable from the network adapter for a minute to re-acquire the IP address). Make sure that the IP address on your network adapter has now been assigned from the subnet 10.10.10.x and that the web interface of the Keenetic router is now accessible via the IP address 10.10.10.1.
After this setting, the Keenetic router should connect to the wireless network of the GPON modem and automatically obtain an IP address from it. You can verify that the IP address has been obtained on the 'System dashboard' page. If the IP address has not been obtained, go to the 'Internet' -> 'Wireless ISP' page and make sure the 'IPv4 configuration' under 'IP address' is set to 'Automatic (DHCP)'.
With this connection option, you will create your own home network (10.10.10.x) independent from the GPON modem so you can manage it yourself (create access lists, have your own DHCP server, set up the firewall, create a guest Wi-Fi network, etc.). You will also be able to improve the quality (level) of the signal in the remote rooms of the flat, where the Wi-Fi signal is weak. You will be able to use AdGuard DNS, CleanBrowsing, Cloudflare DNS, Neustar UltraDNS Public, OpenDNS and Quad9 Internet filters for home network users to ensure secure access to Internet resources.
Option 2
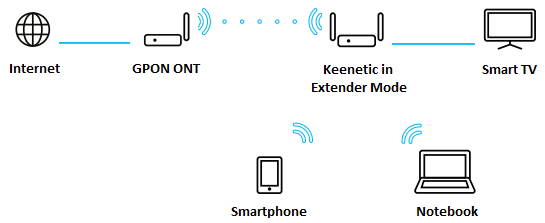
Consider a scenario where the Keenetic router is connected to a GPON modem via a Wi-Fi wireless network and configured in the optional Extender Mode. In this operating mode, the router will pass through data from the GPON modem to your home network clients.
Clients connected via Wi-Fi or Ethernet cable to Keenetic will receive IP addresses from the GPON modem, i.e. all home network devices will be on the same subnet.
NAT and DHCP server will be switched off on the Keenetic device.
Keenetic in Extender Mode will need to connect and get an IP address from the main router. This IP address can be viewed in the GPON modem web configurator (or by using an application to scan and identify LAN-connected devices).
With this connection option, you can extend (increase) the wireless network coverage with the Keenetic router and increase the signal level in remote rooms of the flat where the Wi-Fi signal is weak. At the same time, clients connected to Keenetic via Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi will receive IP addresses from the GPON modem and will have access to all the resources of your home network as if they were connected directly to the GPON modem.
Note
Please refer to the additional articles for further information:
Internet drops when Keenetic is connected through a GPON router?