Keenetic Skipper 4G (KN-2910) has connectors on the housing for external broadband LTE/4G antennas (for the built-in LTE/4G/3G modem). The package includes two removable LTE antennas (for more information on them, you can see the 'Characteristics of supplied removable LTE antennas' article).
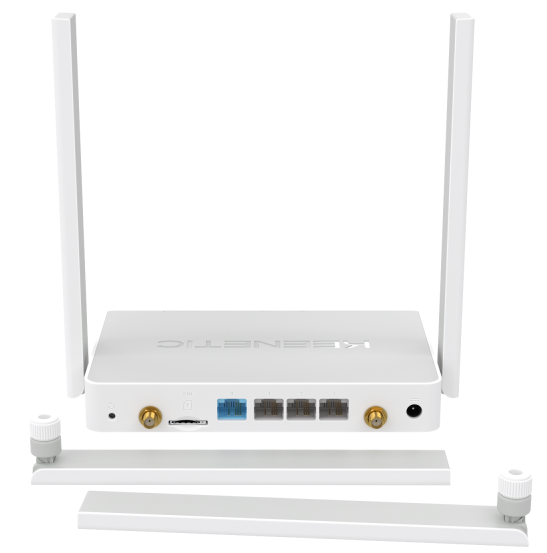 |
The optional outdoor MIMO antenna (with two wires) or SISO antenna (with one wire) can be installed instead of the supplied indoor LTE antennas for operation at greater distances from base stations. The antennas are to be purchased separately.
 |
Recommendations for selecting outdoor antennas
If you know the connection frequency to the base station, it makes sense to use a narrowband antenna. Signals from other frequencies will not degrade the signal quality.
If there is no information about the connection frequency to the base station, it is recommended to connect a broadband antenna.
Check with manufacturers of outdoor antennas connection and installation parameters: antenna gain, cable length, mounting brackets.
In Keenetic routers, the internal path from the built-in modem to the SMA connector has a wave resistance of
50 ohms. It is recommended to connect an external antenna and cable assembly with the same impedance.
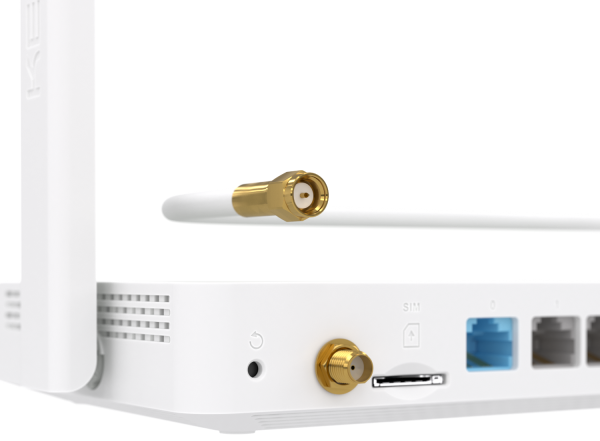
Keenetic Skipper 4G (KN-2910) router use an SMA female connector, and therefore the connected external antenna must be equipped with an SMA male connector.
 |
For more information on SMA connectors, see 'Types of antenna connectors used in Keenetic routers'.
When connecting the SISO antenna, use the following connector on the case.
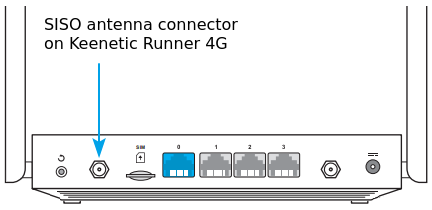 |
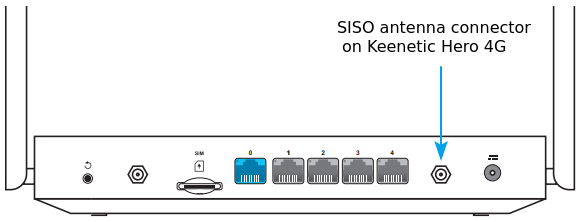 |
The web interface of the router displays the parameters of each antenna.
Go to the Mobile page and under Connection info tap Show antenna information.
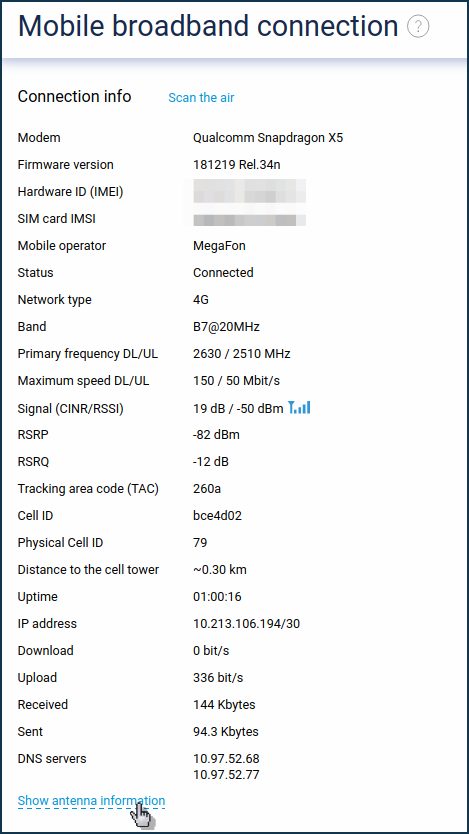
You will see the parameters of each antenna.
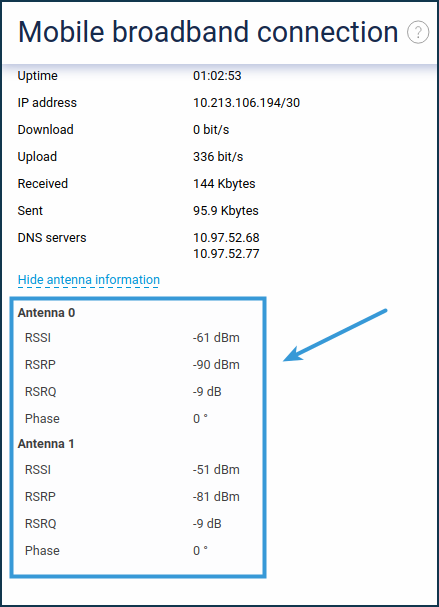
The data in Antenna 0 refers to the SISO antenna connector.
Some outdoor SISO and MIMO (in other words, two SISO antennas in one housing) antennas have markings on the cable connectors indicating the polarization direction.
Historically, operators install base stations in urban areas with MIMO antennas of cross polarization (slant polarization at an angle of
+45/-45 degrees), while stations with vertical polarization can be used in non-urban areas.Vertical polarization has shown better efficiency of radio signal propagation when bypassing obstacles than horizontal polarization.
In case the antenna on a base station is vertically polarised, then setting the MIMO subscriber antenna to a linear (vertical and horizontal) polarization position may give a better signal. In this situation, you should connect the connector on the MIMO antenna with vertical polarization to the Keenetic router in the Tx/Rx connector (it is also called the SISO antenna connector) and with horizontal polarization in the Rx connector.
As a rule, the design of outdoor MIMO antennas allows installation with both linear (picture on the left) and cross polarization (picture on the right):
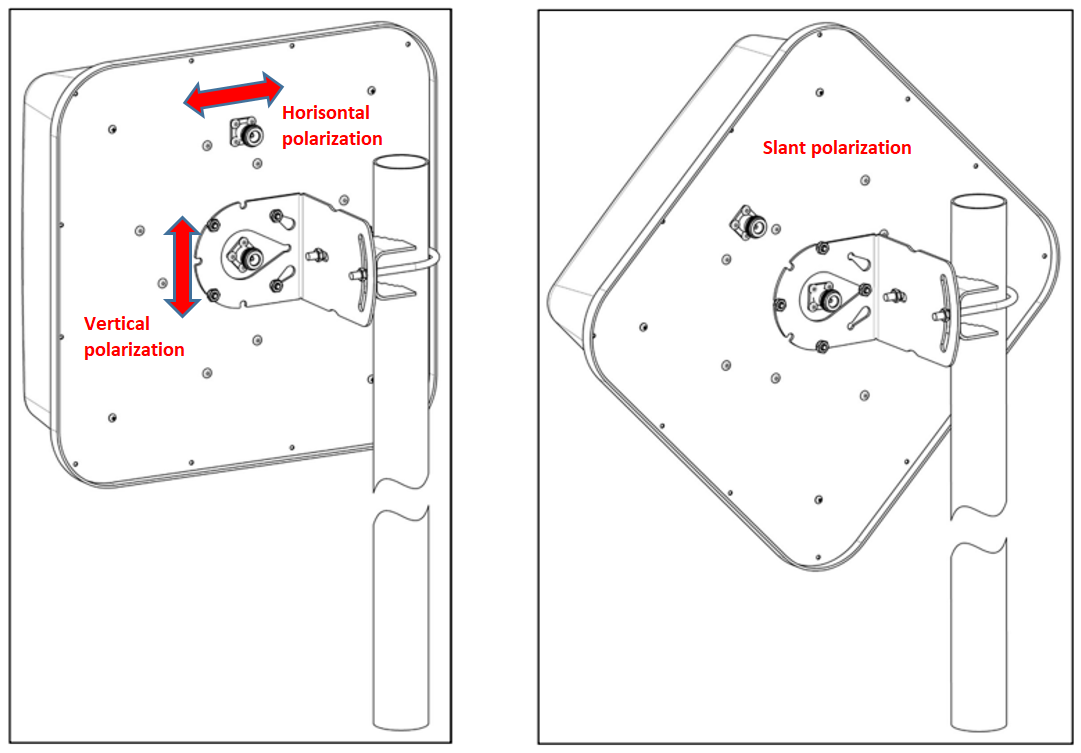
The above example shows the vertical and horizontal polarisation directions for the Krox KAA15-700/2700 and KAA15-1700/2700 antennas.
Usually manufacturer marks the connectors (inputs) on the outdoor MIMO antenna with the direction of polarisation.
In the command-line interface (CLI) of the router, there is a command to scan neighbouring base stations, and by turning the antenna, you can try to connect to them.
The
show interface cellscommand will show a list of mobile network base stations.Command syntax:
(show)> interface <name> cells<name> — full interface name or alias; the list of available interfaces can be seen with the interface [
Tab] command. The built-in 4G/3G modem default interface name isUsbQmi0.Example output of the command results:
show interface UsbQmi0 cellscells: phy-id: 6f rssi: -64 cells: phy-id: 66 rssi: -76