Multipathing (summing the bandwidth of multiple Internet connections)
Starting with KeeneticOS 3.9, smart traffic balancing is implemented when multiple Internet connections are used. In Keenetic routers, this mechanism is called Multipath Mode.
In the router's web interface, you can create a new multipath policy that will optimize the use of several Internet connections and speed up and balance traffic.
In multipath mode, all connections included in the policy automatically transmit traffic. This mode can be used to aggregate the bandwidth of your ISPs.
Note
The most effective balancing will be applied to multi-threaded traffic (point-to-multipoint or one-to-many connections), such as torrent traffic, P2P or other protocols that open multiple connections that do not require keeping the source address. In this case, the connections will be distributed across different connections.
For point-to-point or one-to-one connections, balancing will not work correctly because most hosts will drop packets from the same session if they come from different IP addresses. For example, an Internet site or web service running the HTTPS protocol and opening multiple sessions may refuse to work because if some of the sessions go to different ISPs, it will cause security triggers and errors for the HTTPS protocol.
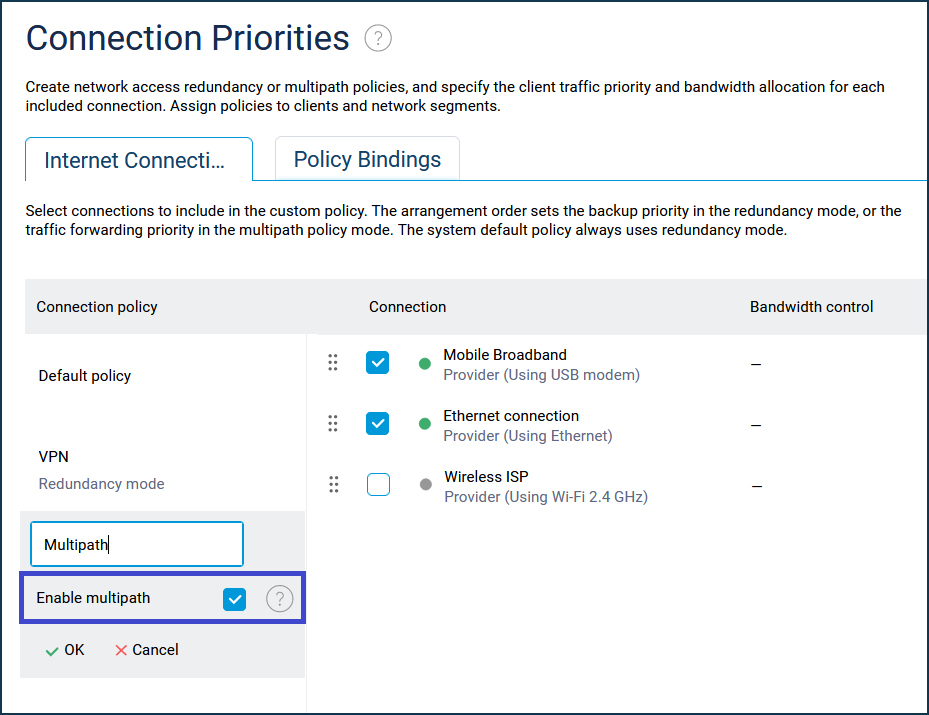
Multipathing can only work under an optional policy (you cannot enable this mode in the Default Policy). To configure it, follow the steps below:
Connect multiple Internet connections to the router (for example, these can be either wired connections or 4G/3G modem connections);
Please note that ISPs should give the Keenetic WAN router IP addresses from different subnets to avoid conflicts
On the Connection Priorities page, add a new policy;
Activate the 'Enable multipath' option and tick the desired internet connections;
Move the device on which you want to get the aggregated speed of multiple connections to this policy;
Check the functioning of multipath transmission. The easiest way is to start downloading a file via a torrent client on your PC. The device will be able to use several connections simultaneously unless of course both providers block BitTorrent peer-to-peer network protocol (in mobile operators' networks, torrent traffic may not work, or it will be artificially limited in speed).
Note
As of KeeneticOS 3.9, the number of sessions is not distributed in the ratio of ip global priorities but in the ratio of physical interface speeds. So, if you have two Gigabit connections, the sessions will be divided in half. And if the first connection is 1000 Mbit/s and the second one is 100 Mbit/s, the ratio is 10/1. Only the speeds of physical links of the ports used are taken into account. Provider's shaper speed limitations under the tariff plan are not taken into account.
It is important to understand that the number of sessions ratio does not guarantee the speed ratio. These ratios approach each other in case of a large number of homogeneous sessions. If the main load is created by a single session, it can be randomly established through any connection. In this case, the speed will be determined only by the speed of that connection alone.
Another innovation of KeeneticOS 3.9 is the possibility to distribute sessions to connections not only on the IP source / IP destination pair basis but also considering udp/tcp source / destination port. The new distribution mode allows sessions to be established between two identical IPs through different connections, which makes channel utilization more even.
Let's show an example of checking the bandwidth aggregation of two Internet connections.
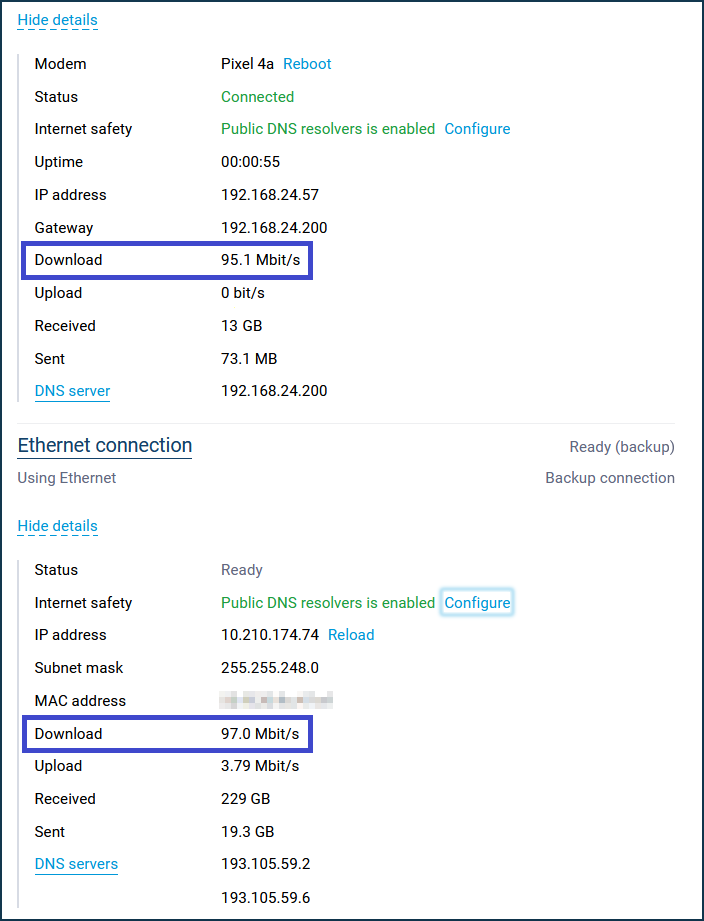
In the web interface, on the System Dashboard page, check the download speed on active Internet connections. In our example, the channel rate for each connection is up to 100 Mbps = 12.5 MB/s.
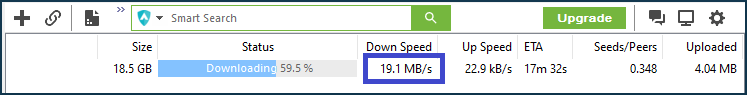
We start downloading a file, and in the torrent client, we see that the download speed is summed up from two Internet channels. In our example, we get the speed up to 20+ MB/s:
Note
For router models with KeeneticOS 2.14 ~ 3.8, you can set up balanced mode connections through the router's command-line interface (CLI). See Using multiple WAN connections in load balancing mode.