Traffic classification and IntelliQoS
Starting with KeeneticOS 3.7, the updated Traffic Classification Engine serves as the base for the IntelliQoS implementation. This service helps to identify the Internet traffic of more than 2,200 applications and 470 application layer protocols. Applications include Slack, Google Meet, PUBG, GeForce Now, YouTube, WhatsApp, Telegram and others; examples of recognised application protocols are FTP, MPEG, PlayStation Network, RDP, SIP, RTP, GRE, ISAKMP, IPsec, L2TP, etc. The IntelliQoS can then apply traffic prioritisation rules to the groups of categories of recognised data flows.
Important
Support for IPv6 traffic classification and prioritisation starts from KeeneticOS 4.0 onwards.
List of applications and protocols supported by KeeneticOS 4.2.x
List of applications and protocols supported by KeeneticOS 4.3 Alpha 9
Let's take a closer look at the functionality of this service.
To enable the service, you must install the system component 'Traffic classification engine'. You can do this on the 'General system settings' page under 'Component options' by clicking on 'Component options'.

Important
The 'Traffic classification engine' component operates entirely independently and does not make any calls to external services.
Once the component is installed, the menu item 'Traffic Classification & IntelliQoS' appears in the web interface under 'My Networks and Wi-Fi'.
Turn the service switch to the 'Enabled' position to allow the system to analyse and classify Internet traffic.
Once the traffic classification service is enabled, the router will automatically analyse, detect and classify traffic passed between local devices and external networks. Disabling the traffic classification service resets the collected data on network applications and categories.
The information obtained in the analysis process is available in the menu items of the 'Status' section:
Traffic monitor;
Application traffic analyser.
Important
By default, Keenetic routers use special mechanisms to handle internet traffic, accelerators. In Keenetic models based on MT7621 and EN7512/13/16/28 chipsets, the Hardware Network Accelerator module cannot be organised in such a way as to provide transparent access to the transmitted data for the classifier service. This leads to an inability to implement accurate traffic counts for categories and applications in default mode, and in some cases, individual application traffic may not be prioritized using IntelliQoS.
For Keenetic Viva (KN-1910), under 'Management' > 'General Settings' > in the 'Performance options' disable the hardware network accelerator if accurate traffic accounting of categories and applications is required.

When the traffic accelerator mode is changed, traffic history is lost.
If the hardware network accelerator is switched off, only the software network accelerator stays in operation. This can result in maximum performance being reduced by around half.
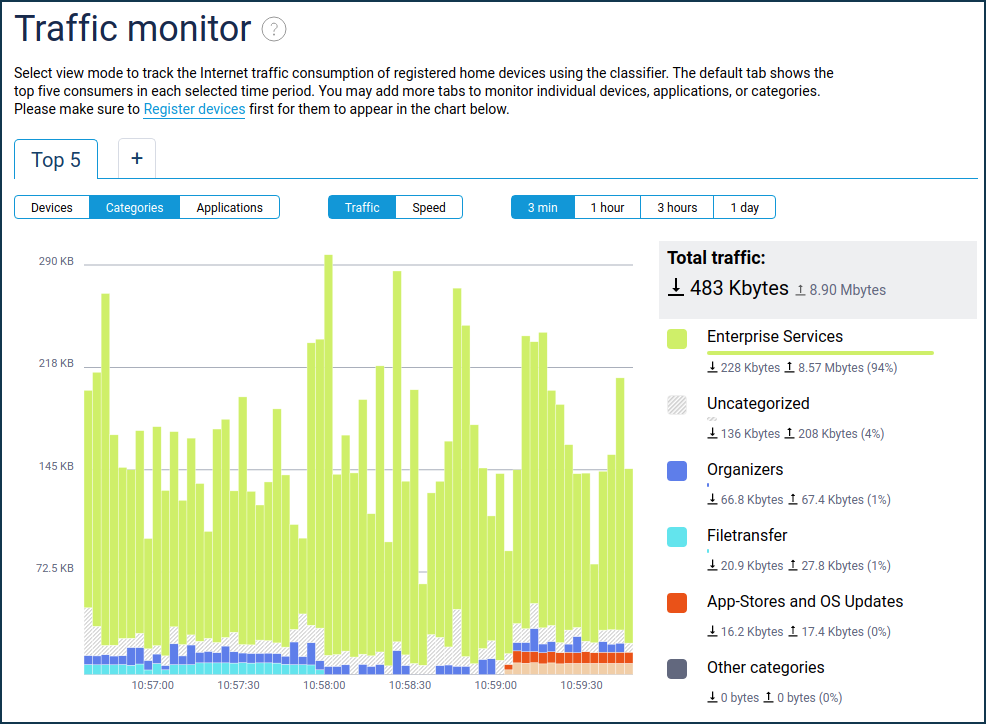
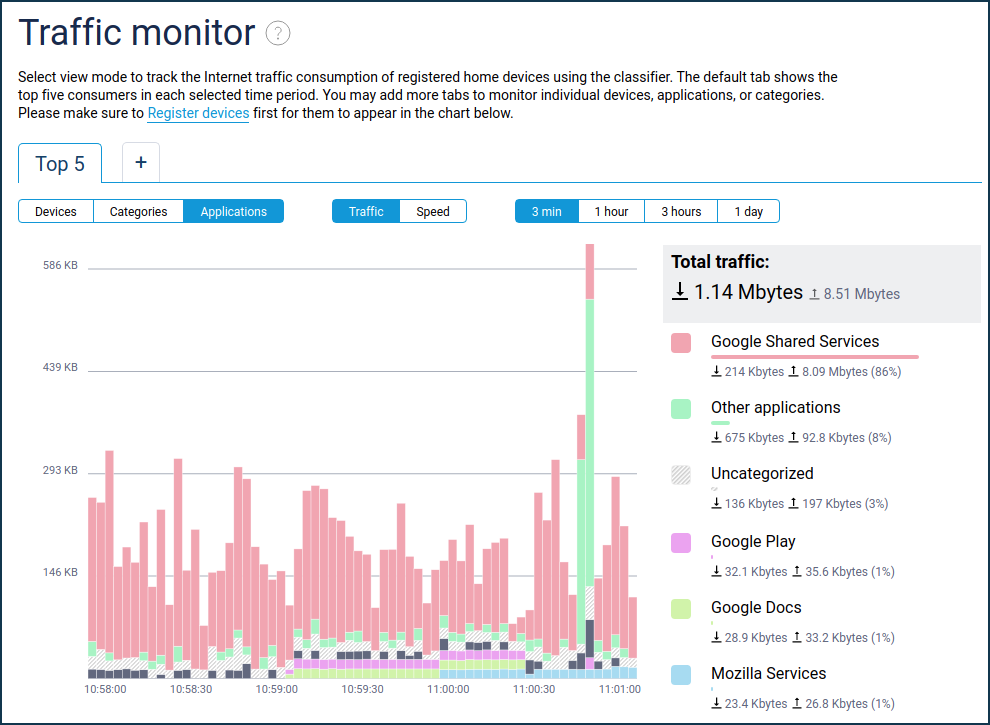
Traffic monitor
The 'Traffic Monitor' menu item provides an additional option to monitor Internet traffic consumption by application categories and individual applications on a timeline of the selected scale.
Application traffic analyser
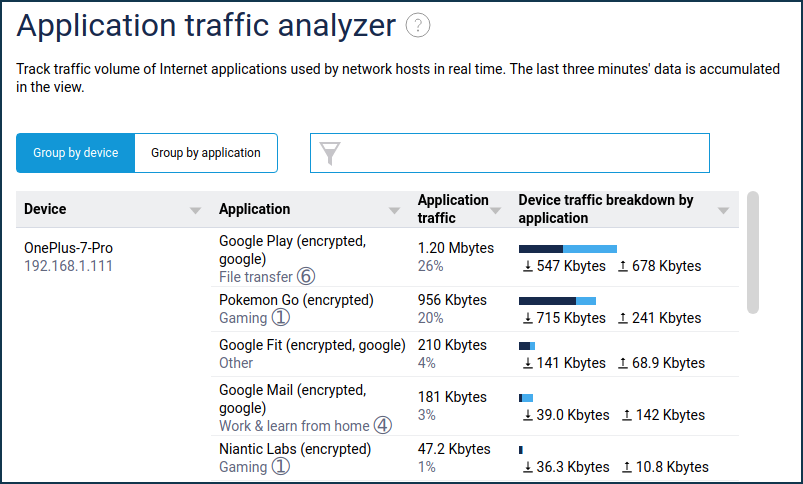
The 'Application traffic analyser' menu item displays the current allocation of Internet channel usage, with the ability to choose the sorting mode — by device or by application.
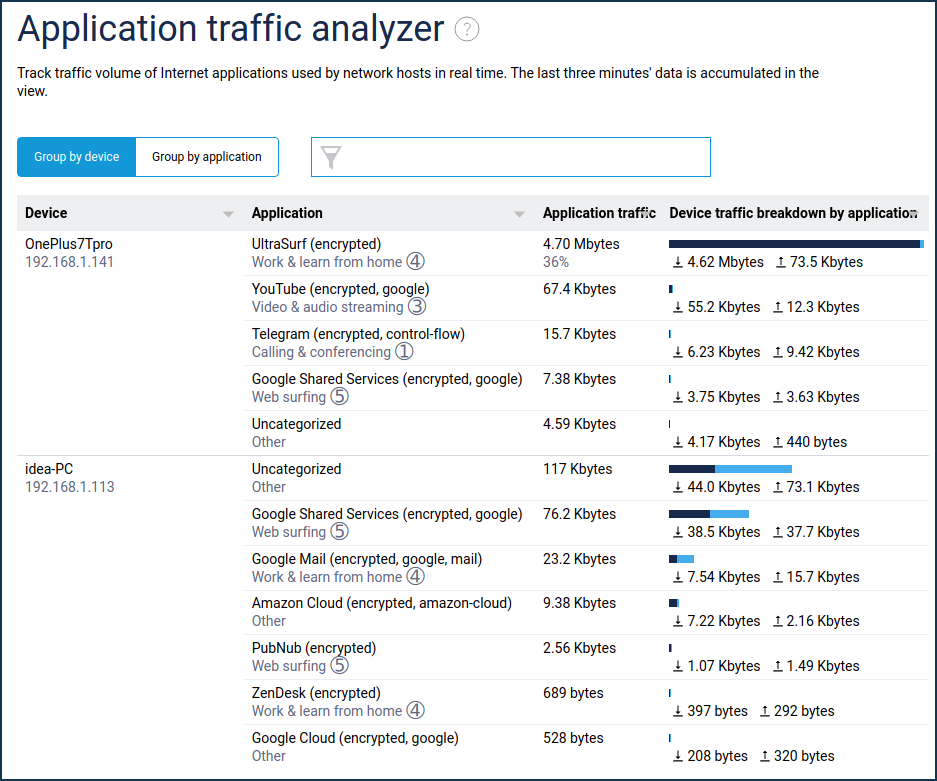
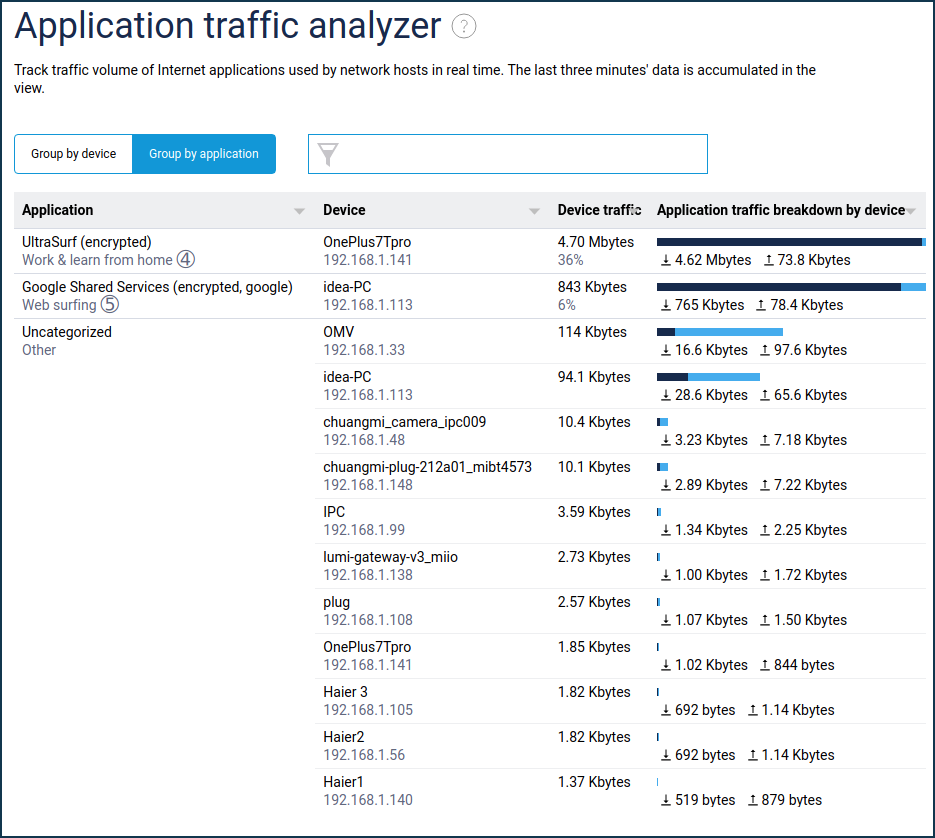
This screen displays a list of hosts that have active internet sessions and, for each host, a list of active applications with real-time traffic volume over the last 3 minutes. Only active applications that currently have traffic are shown. As soon as the connections are closed, the application is removed from the list.
In addition to the recognised application and the amount of traffic, the application category and the transmission priority used for it are also displayed according to the IntelliQoS settings. This view allows you to see that the applications are recognised, and the traffic is prioritized.
IntelliQoS
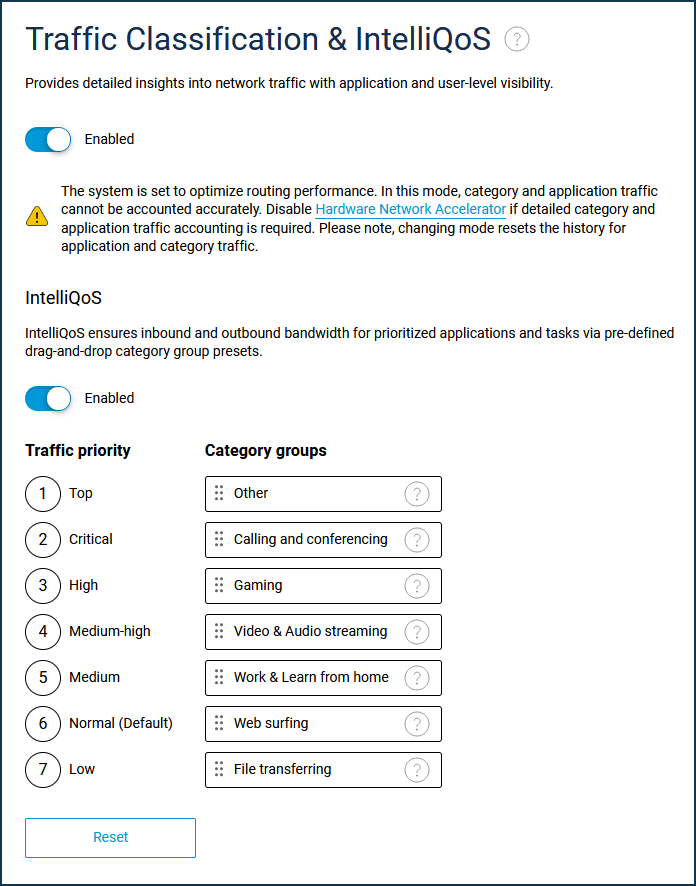
Under the menu item 'Traffic Classification & IntelliQoS', the IntelliQoS function automatically assigns traffic priority to groups of network application categories.

IntelliQoS requires that the traffic classification service is also enabled.
Important
IntelliQoS Priority will only be applied to the application traffic of those home network devices for which no Class of Service (default) is set in the Client lists. For devices with a service class set, all applications will use that class, regardless of the settings on the IntelliQoS page.
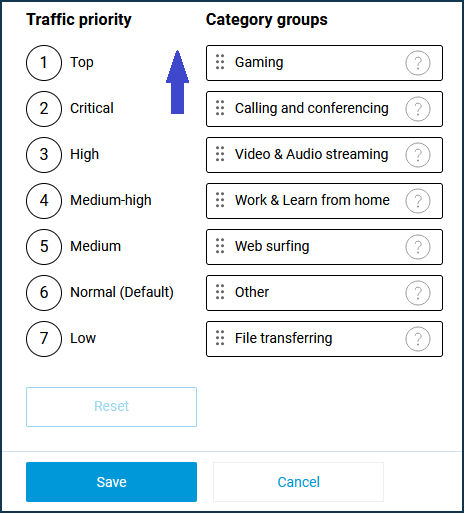
The built-in traffic categorisation system uses six primary groups of network traffic, plus the 'Others' group, formed on a residual basis. Each group can correspond to one of the levels of traffic processing priority.
Note
There are 7 levels of prioritization available in IntelliQoS; a higher number corresponds to a lower priority. By default, traffic groups are prioritized as follows:
➀. Top
Group: Calling and Conferencing
Includes categories: Voice over IP, Messaging, Mobile Data, Conferencing;
➁. Critical
Group: Gaming
Includes Gaming category;
➂. High
Group: Video & Audio streaming
Includes categories: Streaming, Audio Entertainment, Multimedia Service Providers;
➃. Medium-high
Group: Work & Learn from home
Includes categories: Tunnels, Business, E-commerce, Remote Management, Mail, Databases, Finance, Education, Organisers and Information Management, Machine-to-Machine and Internet of Things (IoT);
➄. Medium
Group: Web surfing
Includes categories: Web, Social Networking, News, Navigation, Device Security, Corporate Services, Browsers;
➅. Normal (Default)
Group: Other
Includes categories: General, Network Management, Obsolete, Industry, Encrypted, Advertising and Analysis Services, Health and Physical Education, Cloud CDN Services, Travel and Transportation, Books and Magazines, Deleted, Moved;
➆. Low
Group: File transferring
Includes categories: Peering, File Transfer, Virtual Hosting, App Stores, and OS Updates.
Let's take an example.
Suppose you want to increase the priority of games for all devices in your home network.
Ensure that the required hosts do not use separate prioritization of all traffic according to the established class of service.
Drag the 'Gaming' category group to the top of the list with the mouse, set it to the highest priority ➀, and apply the setting by clicking the 'Save' button.
In the 'Application traffic analyser' menu, you can see the prioritization of 'Pokemon Go' application traffic (category 'Gaming') according to the priority selected for the 'Gaming' category group.