KeeneticOS 3.6
KeeneticOS 3.6.12
21/10/2021
Fixed
Fixed a nasty bug that caused KeeneticOS to crash and device to reboot during the update availability check under certain conditions. [NDM-1830]
KeeneticOS 3.6.11
01/09/2021
Fixed
There are no changes for Keenetic Speedster (KN-3010).
KeeneticOS 3.6.10
20/07/2021
New
There are no changes for Keenetic Speedster (KN-3010).
Fixed
Fixed the procedure for Extender acquisition to the Mesh Wi‑Fi System under certain conditions. [NDM-1775]
KeeneticOS 3.6.9
08/07/2021
Improved
We deployed a new firmware signing certificate to the cloud infrastructure to strengthen the security of KeeneticOS updates. [SYS-314]
Fixed
There are no changes for Keenetic Speedster (KN-3010).
KeeneticOS 3.6.8
28/06/2021
New
There are no changes for Keenetic Speedster (KN-3010).
Improved
Updated
Curldaemon to7.77.0version, which fixes the CVE-2021-22897, CVE-2021-22898, CVE-2021-22901 vulnerabilities.
Fixed
There are no changes for Keenetic Speedster (KN-3010).
KeeneticOS 3.6.6
27/05/2021
Improved
Patched a collection of security vulnerabilities called FragAttacks (Fragmentation and Aggregation Attacks). [SYS-276, SYS-277, SYS-278, SYS-280, SYS-282, SYS-283]
CVE-2020-24586 — fragment cache attack (not clearing fragments from memory when (re)connecting to a network).
CVE-2020-24587 — mixed key attack (reassembling fragments encrypted under different keys).
CVE-2020-24588 — aggregation attack (accepting non-SPP A-MSDU frames).
CVE-2020-26139 — forwarding EAPOL frames even though the sender is not yet authenticated (should only affect APs).
CVE-2020-26146 — reassembling encrypted fragments with non-consecutive packet numbers.
CVE-2020-26147 — reassembling mixed encrypted/plaintext fragments.
CVE-2020-26140 — accepting plaintext data frames in a protected network.
The security issue CVE-2020-15078 of the OpenVPN client and server system component.
Fixed
Internet safety policy operation after re-establishing a PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) connection to the Internet. [NDMS-1420, NDMS-1485]
KeeneticOS 3.6.3
05/04/2021
Improved
Updated to the latest OpenSSL library version 1.1.1k, which fixes the CVE-2021-3449, CVE-2021-3450 vulnerabilities.
Fixed
There are no changes for Keenetic Speedster (KN-3010).
KeeneticOS 3.6.2
22/03/2021
Fixed
There are no changes for Keenetic Speedster (KN-3010).
KeeneticOS 3.6.1
11/03/2021
New
Improved compatibility and security: The EAP-PEAP authentication is implemented for both server and client components of the IKEv2 VPN, providing extended compatibility and stronger security. [NDMS-1324]
The
aes256-sha256-modp2048mode for IPsec connection is now enabled for better compatibility with the ProtonVPN service provider. [NDMS-1004]
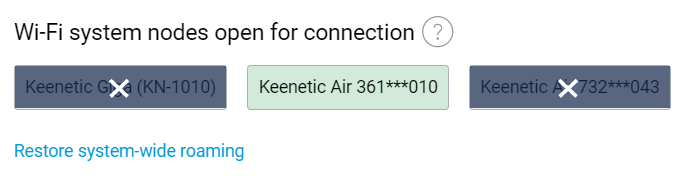
The roaming area for wireless clients can now be restricted. By default all wireless clients can roam between all Wi‑Fi system nodes. This may introduce issues with sticky wireless clients in stationary Wi‑Fi-connected appliances like Smart TV. Sticky client remains connected to a distant node when there is better node nearby. This can severely impact the performance of device itself and Wi‑Fi network at whole. To address this issue you can now specify for for particular sticky wireless client the list of Wi‑Fi system nodes it can connect. The setting is available in both CLI and web interface on the Registered devices options page. [NDMS-1311]
mws zone {mac} {cid}— limits zone for the device with the specific MAC address to the nodes of the Wi‑Fi system with the specific cid in the CLIor choose Wi‑Fi system nodes that will deny connection for a particular device in the web interface
If you don't want the LED indicators of your device to operate all day and night, you can use the new handy LED indicators control feature, available on the General system settings page of the web interface. It allows you to set up separate operating schedules for the LED indicators on your device's front and back. [NDW-1700]
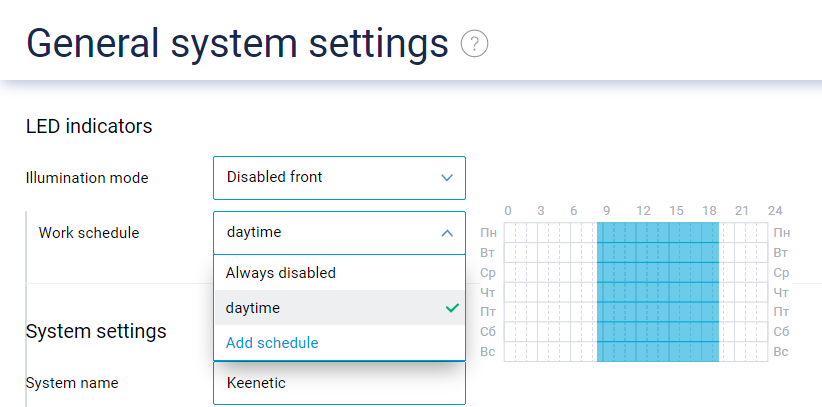
The power-down schedule for LED indicators is now inverted. [NDMS-1265]
Do not use the obsolete command
system led shutdown {mode} schedule {schedule}.Instead, issue these new commands in the CLI to apply the setting:
system led power schedule {schedule}— apply the LED indicators power-up schedulesystem led power shutdown (front | back | all)— apply the LED indicators shutdown mode
A new feature for HTTP header enforcement is added. It can be used when you cannot access the web application in your home network remotely. [NDMS-1259]
Issue this command in the CLI to apply the
force-hostheader value to the corresponding domainnameip http proxy {name} force-host {force-host}
The debugging mode of STP processing is implemented, providing detailed information on Wi‑Fi system operations. It can be requested by the technical support engineer for additional diagnostics. You don't need to enable it for day-to-day operations. [NDMS-1204]
mws log stp {interface}— enable STP debugging on the bridgeinterfaceno mws log stp {interface}— disable STP debugging on the bridgeinterface
A new PPPoE connection recovery algorithm is implemented. The series of multiple PADO packet timeouts now triggers the link restart action on the WAN Ethernet port of the device, restoring the remote equipment's correct port operation, and speeding up the re-establishment of the PPPoE connection. [NDMS-1179]
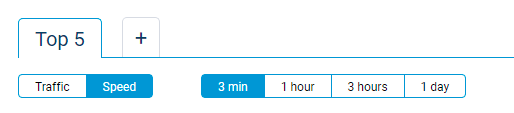
A new selector for Speed monitoring is added on the Host traffic monitor page. Use it to observe the speed of Internet connection for your home network clients over specific periods of time. [NDW-1580]
It is possible to set the description of your device's Ethernet ports using the
interface {interface} description {description}command in the CLI. Now this description is displayed inside the icons of the Network ports section on the web interface's System dashboard page. If the description is longer than four symbols, then only three first of them are displayed inside the icon. To display the whole string, hover the cursor over the port's icon. [NDW-1594]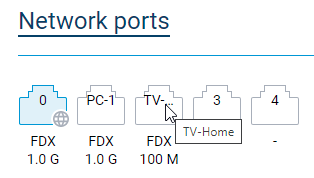
A static IP address can now be assigned to the Extender device in the web interface of the Controller device. [NDW-1520]
Open a particular Extender's node settings in the Members list on the Wi‑Fi system page and apply the desired IP address.
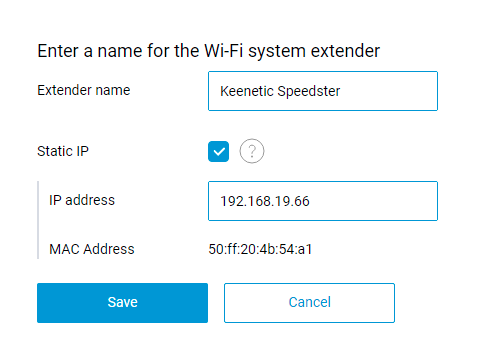
Note
If the static IP address differs from the address currently used, you will need to reconnect or reboot this Extender device for the new setting to be applied.
Advanced Wi‑Fi settings of extender nodes now allow changing Channel width for radio interfaces shared with mesh back-haul connections. [NDW-1495]
The new algorithm now automatically switches the Beeline ISP's Internet connection types from L2TP to IPoE.
IKEv2 tunnels now feature DHCP Option 249 support. This delivers the static routes setting from the tunnel server-side to the remote clients in
DHCP INFORMpackets for automatic configuration. [NDMS-686]
A new scanning algorithm for the wireless environment is implemented. It starts once a new Extender device is added to the Mesh Wi‑Fi system and lets all nodes determine the proper neighbors for wireless back-haul connection. [NDMS-1087]
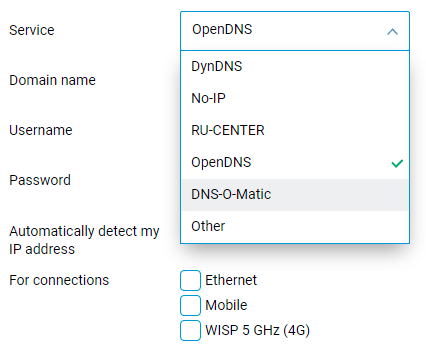
If your device has a public IP address, you can access it remotely using a convenient static domain name registered by a DDNS provider. The setting for OpenDNS and DNS-O-Matic DDNS providers is now supported. It is available within the DDNS tab on the web interface's Domain name page. [NDMS-1010]
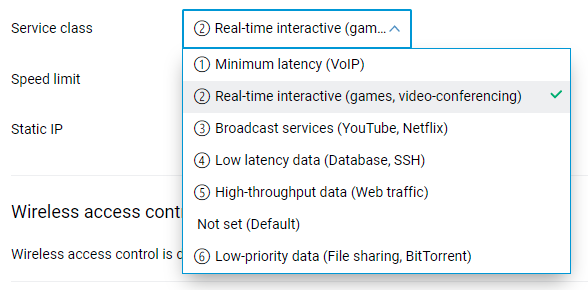
The traffic Service class can now be applied to a registered device in the web interface. It defines the data processing priority for the particular device. When the ISP connection is reaching its utilization cap, requested bandwidth is allocated first for devices having higher priority. For instance, you can apply a higher priority service class to the host experiencing voice calls delays or online video freezes while another host is downloading files. [NDW-1347]
Note
N.B.: The higher priority setting has a lower number value in the Service class drop-down list.
The Network ports settings list in the web interface is enhanced by additional auto-negotiation options providing improved compatibility. [NDW-1370]
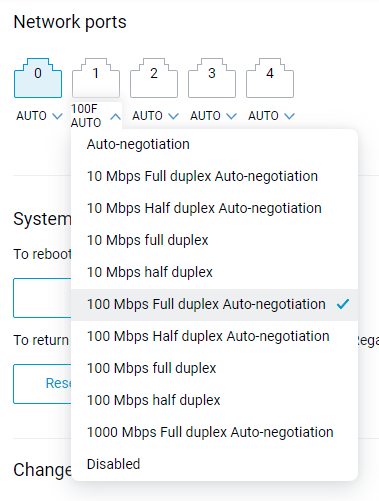
Improved
The
show ip name-serverCLI command now displays the DNS server list from all Internet connections, with corresponding system interface naming. [NDMS-1415]
Dynamic selection algorithm of the best up-link node for the wireless back-haul connection has been improved. It is now more sensitive to other Mesh Wi‑Fi system's node signal strengths, increasing the bandwidth and stability for wireless interconnections. [NDMS-1411]
IPv6 address detection for local hosts is improved. The problem of periodic Internet connection loss on registered local devices using IPv6 addressing when the strict No internet access setting is enabled on Connection policy for unregistered devices is now fixed. [NDMS-433]
A new pool for improved management of PMK-R1 keys is implemented. This change fixes the unstable connection of some wireless clients using WPA3 security while roaming between the nodes of your Wi‑Fi system. The fast and seamless transition mechanism, improving the usage of applications sensitive to packet delay and drops, is now completely available for WPA3 clients. [NDMS-1236, NDMS-1253, NDSM-1258, NDMS-1272].
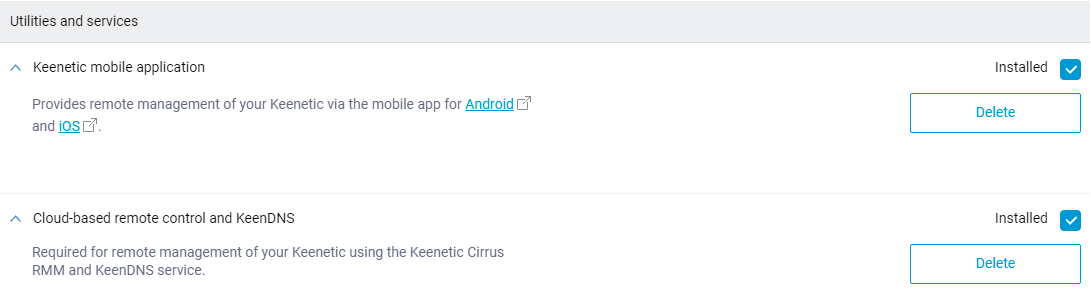
To give you more granular control of KeeneticOS features, we have separated the Keenetic mobile application and the Cloud based remote control and KeenDNS components. If the mobile application is not used, the corresponding component can now be removed from KeeneticOS completely. [NDMS-1174]
Improved security: The OpenSSL library is updated to version 1.1.1i. It fixes the CVE-2020-1971 vulnerability.
Mesh Wi‑Fi system extenders now have unique local MAC addresses in each network segment. This improves Wi‑Fi system operational stability, especially when connecting extenders via unmanaged Ethernet switches. [NDMS-1083]
Improved timezone setting: Extender devices now automatically apply timezone setting propagated by the Controller device of Wi‑Fi system. You don't need to set the timezone manually per node. [NDMS-1251]
The Host traffic monitor page of the web interface has received minor usability improvements. [NDW-1577]
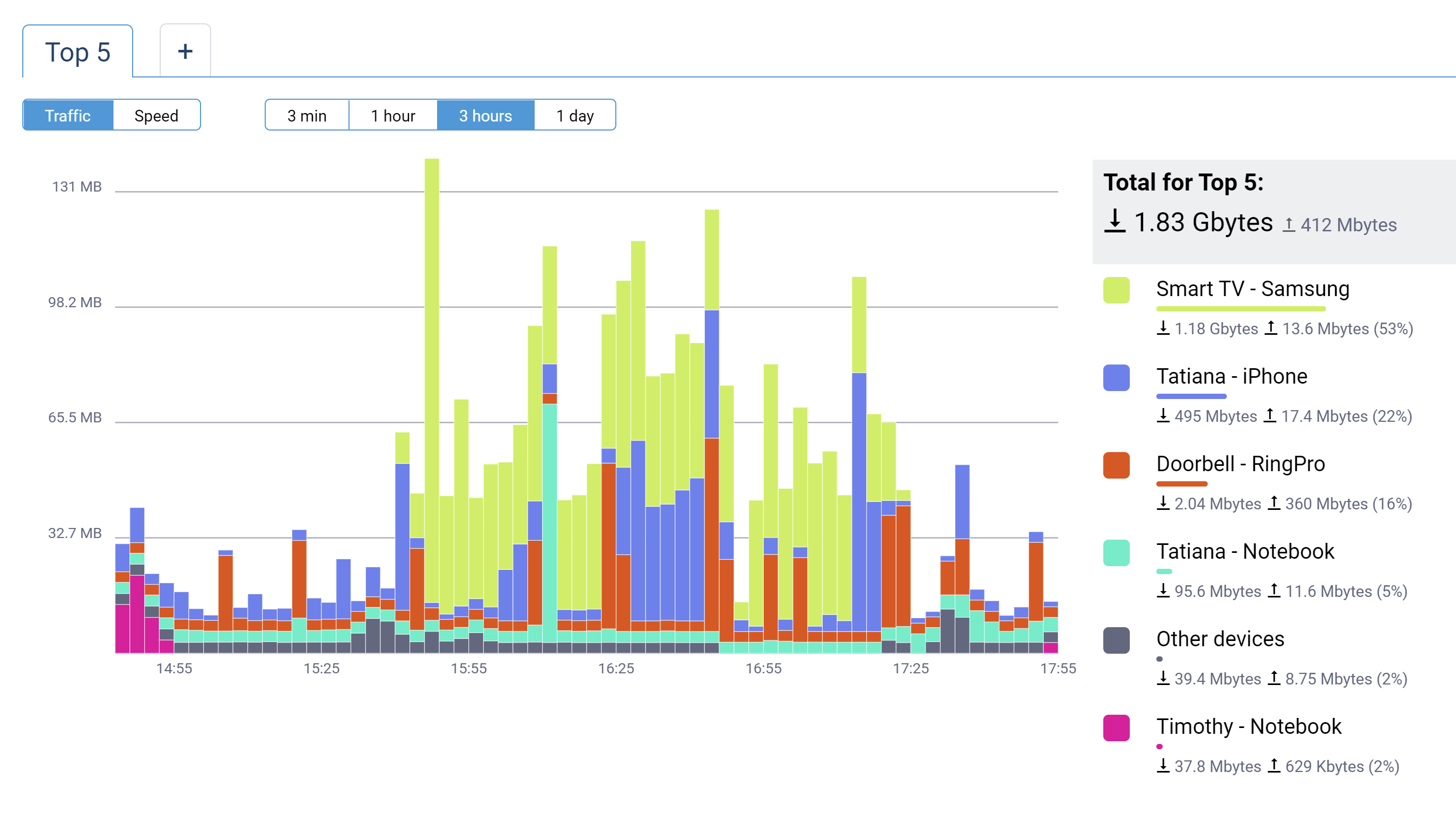
The first tab shows the Top5 highest consumption devices or types of traffic in different colors. The last item in the list, colored gray, is the sum of the traffic from all Other devices that in total consume less than any one of Top5. The multicast traffic is shown separately from this item only when its amount becomes one of Top5. Otherwise, it is included in Other devices item. You can also add more tabs for particular registered devices of your home network, for detailed monitoring.
The IPsec protocol code was updated to remove obsolete elements, and to optimize the footprint, providing improved tunnel connection security, stability and compatibility. [NDMS-268]
The Mesh Wi‑Fi system Extender device's best path selection algorithm for wireless back-haul connection is improved. This change now provides greater stability and performance of the Mesh Wi‑Fi system's nodes interconnections. [NDMS-1120]
The Protected Management Frames (PMF) feature is now enabled on wireless back-haul interconnections of the Mesh Wi‑Fi system's nodes, improving network security and protection against disconnection attacks by intruders. [NDMS-951]
Fixed
A huge configuration file with a size exceeding 65639 bytes could not correctly download from or upload to the Keenetic device. [NDMS-1455]
Wi‑Fi System Extenders with Mesh Wi‑Fi backhaul links may not forward wireless or wired clients' traffic correctly under certain conditions. [NDMS-1175]
The bug that didn't allow the addition of the Extender device to the Wi‑Fi System is fixed.
The display of the
force-host: not enough argumentserror in the startup configuration is fixed. [NDMS-1259]
A seamless Wi‑Fi roaming improvement is made: The unstable fast transition of wireless clients in Guest segment is fixed. The issue affected all network segments with the
protectedsecurity level setting. [NDMS-1244]STP processing is disabled for OpenVPN and EoIP interfaces included in the Bridge type of interface. This change prevents unstable behavior of the Wi‑Fi system triggering drops of the tunnel connections. [NDMS-986]
The bug in domain name processing is fixed. Now clients of your home network can correctly resolve the domain name of the Keenetic device booked with KeenDNS service. [NDMS-1250]
Wireless clients, roaming to the nodes of a Mesh Wi‑Fi system using a fast transition mechanism, could experience connection problems when the GTK (Group Temporal Key) renewal happened. An improvement, applied to the GTK re-keying procedure, resolved the connection stability for such clients, ensuring seamless roaming. [NDMS-1205]
Minor fixes in the appearance of the web interface's Device lists page. [NDW-1477]