What is the Wi-Fi System?
Why a Wi-Fi system?
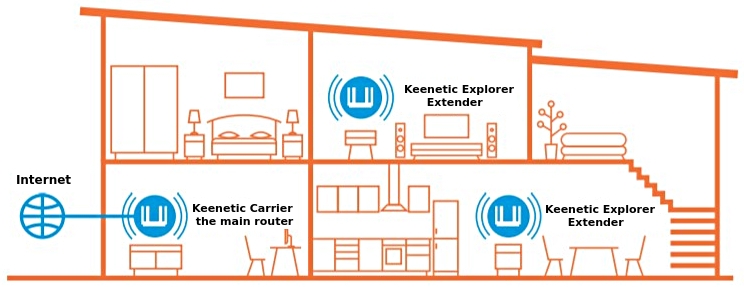
Covering a multi-room or multi-level space with one Wi-Fi router is often impossible. Walls, partitions, doors and furniture all obstruct the Wi-Fi signal from your router to your client devices. To extend your wireless coverage, you don't need to find the perfect spot for a single router; add one or more of our Keenetic routers as Extenders wherever you need them. It's the easiest and most effective way to extend your wireless network.
Extenders can be connected not only over Wi-Fi via mesh but also over the wire: directly to the Main Router or through an additional switch, in a star or daisy chain topology.
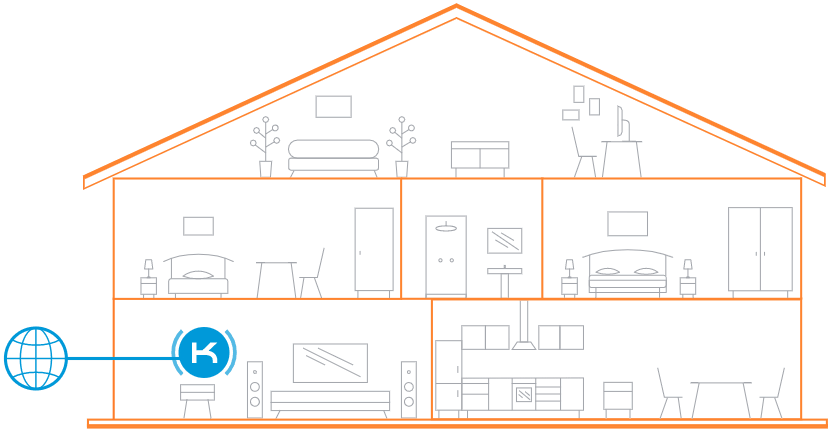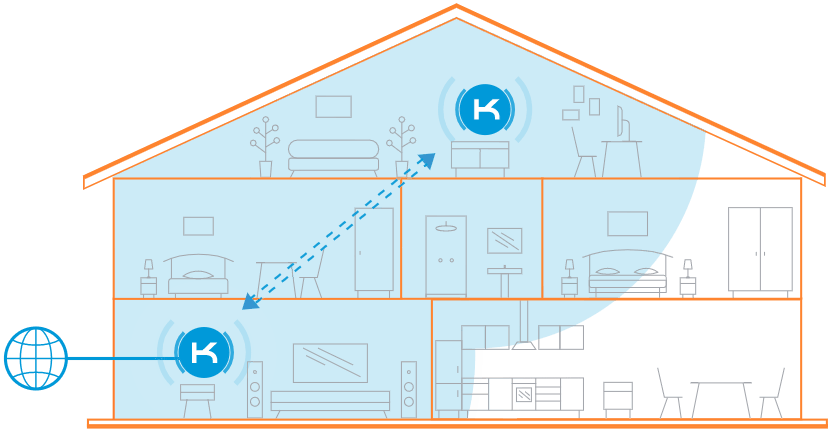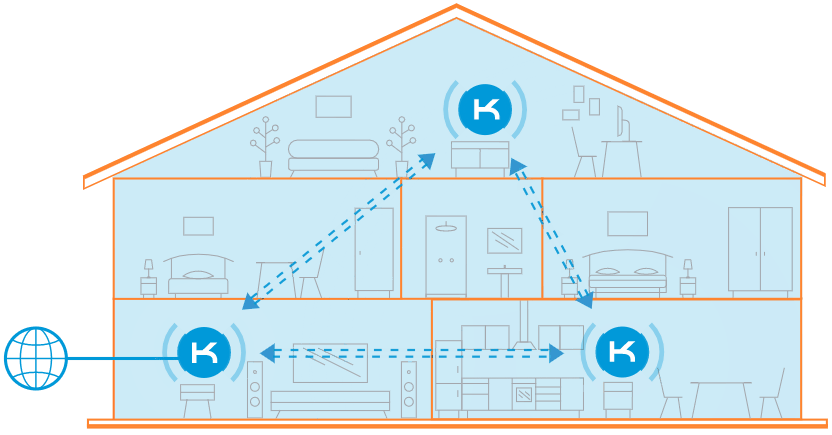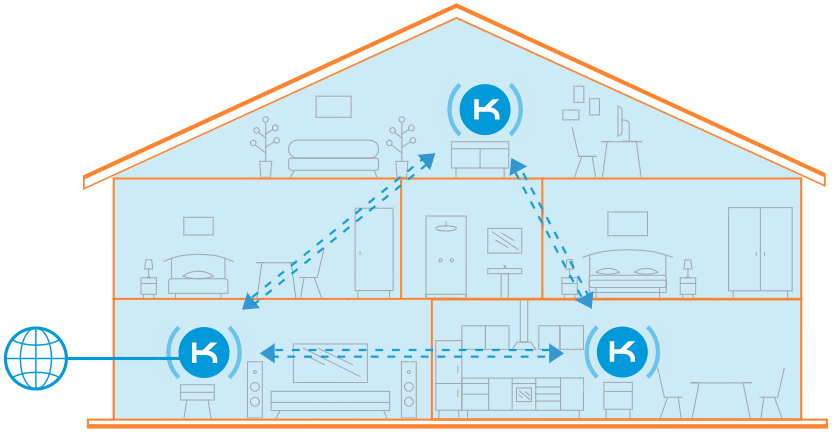
Keenetic routers, combined into a Mesh Wi-Fi System, create a seamless network throughout your home or office.
Note
The term 'Extender' refers to a Keenetic device in a universal operating mode, which combines an Access Point and a Repeater, and is added to a single Wi-Fi System.
Depending on the connection method (cable or Wi-Fi), the device automatically detects the correct operating mode. If the Extender is connected to an existing network via Ethernet cable — the 'Access point' mode is used; if the Extender is connected via Wi-Fi — the 'Repeater' mode is used.
When you need more coverage, just add as many additional Keenetic extenders as necessary.
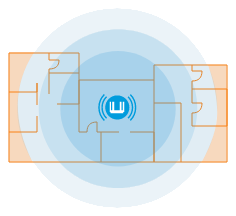
Do not try to cover a multi-room or multi-level space with a single router. For example, in the 5 GHz band, this is not possible in principle. Better yet, add one or more Keenetic routers as extenders where needed.
A single router does not provide full coverage:
Keenetic Mesh Wi-Fi System multiplies coverage:
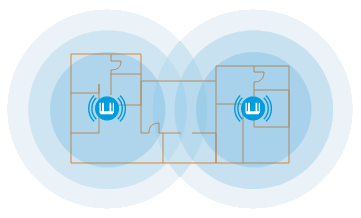
This allows you to connect multiple Keenetic routers into a single wireless network with one name and password for both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. You can add as many access points (extenders) to your Wi-Fi System as you need, extending your Wi-Fi to any distance within the same local area network. 'Seamless roaming' will operate within the whole network, allowing client devices to switch automatically between access points without losing connectivity. In addition to the Home and Guest networks, any other network segments are also extended, and all USB applications (connection of external drives, disks, printers, DLNA media library, Download Station, CIFS/SMB, FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, etc.) are kept running on the extenders.
You can find more information in the 'Setting up Mesh Wi-Fi System' article.
How does it work?
A Wi-Fi System requires at least two Keenetic routers: one to act as the Main Router (Сontroller) and the others as an additional device (Extender) to extend the Wi-Fi coverage.
Multiple access points are preferred for extensive coverage areas in flats, private houses, or offices. You can combine Keenetic routers into a single wireless network with the ability for clients to roam between 802.11r/k/v access points (Wi-Fi seamless roaming).
Additional Keenetic routers can be added to the Wi-Fi System as Extenders, connecting them over the wire for maximum performance or over Mesh Wi-Fi without the need for cabling.
The Wi-Fi System Controller automatically controls the Extenders, allows additional devices to be added and allows a unified wireless system to be centrally managed and monitored. No Internet connection or cloud services are required for its operation. The Controller works on all actual Keenetic models from Starter to Titan, except Buddy models, which act as Extender only.
Suppose you already have one Keenetic router working as a basic router and need to extend your Wi-Fi coverage. Add another Keenetic to your network by connecting it via Ethernet cable to your router or via Mesh Wi-Fi, pre-setting it to Extender Mode.
Note
For maximum Wi-Fi performance, connect Extenders over Ethernet.
Once a Wi-Fi System is set up, the wireless settings on the Controller and Extenders will be shared, and there will be no need to configure them separately on each device. Basic Wi-Fi network parameters will be locked for editing on Extenders and can only be changed from the Wi-Fi System Controller. For example, if you want to change the network name (SSID), you only need to change it on the Controller, and it will spread the change to all Extenders. In addition to the Home and Guest network, the Wi-Fi System extends coverage for the smart home and your other additional segments.
Keenetic Wi-Fi System implements seamless 802.11r/k/v roaming rather than simply using the same network name. The mechanism is called Wi-Fi Seamless Roaming and is designed to speed up the switching of wireless clients between access points. When moving within the coverage area, the network client selects the most appropriate access point, depending on signal strength, network load and other factors. This is especially important for a stable connection when using IP telephony and Voice over Wi-Fi technology.
Important
The quality of seamless Wi-Fi roaming is highly dependent on customer equipment and the presence/absence of 802.11r/k/v protocol support. On devices without 802.11r fast roaming protocol support, Keenetic routers can use PMK cache transition.
Mesh Wi-Fi System is based on VLAN technology (to separate network segments) and STP protocol (to select the best connections between nodes). Keenetic supports up to four different Wi-Fi networks. Mesh Wi-Fi automatically creates a separate hidden wireless transport network for communication between nodes (backhaul network). This network is allocated to a particular VLAN segment in the 5 GHz band for dual-band models and the 2.4 GHz band for other models.
When using a dual-band model as an Extender (Explorer, Speedster, Buddy 5/5S), when captured in a Mesh Wi-Fi System, the wireless connection between routers will only work in the 5 GHz band (this is at the moment a current limitation of the Wi-Fi System design).
Using the STP protocol, the system monitors the signal strength of the nodes and automatically configures the mesh network. For example, when one of the Extenders is switched off, the other nodes will automatically reconnect in terms of connection quality. The Extender selects the optimum access point (on other Extender or Main Router) based on its signal strength and metric (distance to Main Router). The same will happen when a new Extender is added to the Wi-Fi System.
When choosing the best connections between nodes, wired connections are preferred. If an Extender is connected via Ethernet cable, the wireless Mesh connection is still established, but data transfer via Wi-Fi is blocked as long as the cable is connected. In an accidental cable break or damage, the Extender will switch over to a wireless mesh connection by itself.
For more information on setting up a Wi-Fi System and adding Extenders to it, see the instructions:
Setting up Mesh Wi-Fi System
An example of creating a Wi-Fi system with two Keenetic routers